|
|||
|
Fall 2022 – INTERNET LAW - Syllabus
Fall 2022 -Internet Law Bick TH 3:55-5:50
Fall 2022 - Internet Law Seminar Credits: 2 Thursday 3:55 pm - 5:55 pm Location Rutgers School of Law 123 Washington St. Newark, NJ 07102–3046
Internet Law Seminar Course Outline and Schedule Class / Date / Topic I August 25 Introduction to the Internet and Internet Law XIV December 2 Student Presentations & special topics WORK PRODUCT DUE Contact information –Jbick@bracheichler.com--- 973-403-3155 (office)
I August 25 Introduction to the Internet and Internet Law
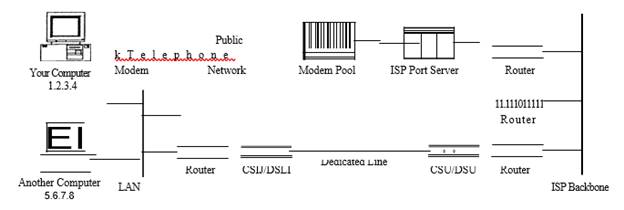
2. "Why Should the Internet Be Any Different" Pace Law Review (Fall 1998) 3. Let’s Get Technical (Course Materials 1 may be found on – see Rutgers Canvas ). Course Materials 1 - Class I Let’s Get Technical Course Materials 1 The Internet is a global network of computers. To achieve this each computer connected to the Internet must have a unique address. Internet addresses are in the form xxx.xxx where xxx must be a number from 0 - 255. This address is known as an Internet Protocol ( IP address). The picture below illustrates two computers connected to the Internet; your computer with IP address 1.2 and another computer with IP address 3.4. Computer 1 Known as 1.2 Internet Computer 2 known as 3.4 When using a dial-up to connect to the Internet through an Internet Service Provider (ISP), usually assigned a temporary IP address for the duration of the dial-in session. If you connect to the Internet from a local area network (LAN) your computer might have a permanent IP address or it might obtain a temporary one from a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. In any case, if you are connected to the Internet, your computer has a unique IP address. Protocol Stacks and Packets Once a computer is connected to the Internet and has a unique address it can send and receive signals from other similarly enabled computers. For example if computer 1.2.3.4 want to send "Hello" to 5.6.7.8 To do so "Hello" must be changed into electronic signals, transmitted via the Internet, then translated back. This process is accomplished using TCP/IP protocol stack. because of the two major communication protocols used. The TCP/IP stack looks like this: Layers Application Protocols Layer Internet Protocol Layer Hardware Layer
Internet Infrastructure Internet communications are sent from a sending computer to an ISP server to a local backbone server to a backbone server to a local backbone server to an ISP server to a recipient computer. The Internet backbone is made up of many large networks which interconnect with each other. These large networks are known as Network Service Providers or NSPs. Some of the large NSPs are UUNet and IBM. How messages are controlled The information used to get communications to their destinations are contained in routing tables kept by each router connected to the Internet. Each router knows which IP addresses they use. The router usually doesn't know what IP addresses are 'above' it. When a packet arrives at a router, the router examines the IP address put there by the IP protocol layer on the originating computer. The router checks it's routing table. If the network containing the IP address is found, the packet is sent to that network. If the network containing the IP address is not found, then the router sends the packet on a default route, usually up the backbone hierarchy to the next router. Domain Names and Address Resolution The Domain Name Service or DNS a distributed database which keeps track of computer's names and their corresponding IP addresses on the Internet. Many computers connected to the Internet host part of the DNS database and the software that allows others to access it. These computers are known as DNS servers. No DNS server contains the entire database; they only contain a subset of it. If a DNS server does not contain the domain name requested by another computer, the DNS server re-directs the requesting computer to another DNS server. Root org corn gov RedCross BickLaw uspto Publications search Application Protocols: HTTP and the World Wide Web One of the most commonly used services on the Internet is the World Wide Web (WWW). The application protocol that makes the web work is Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP. HTTP is the protocol that web browsers and web servers use to communicate with each other over the Internet Note: Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is not HTTP it is a web page maker language. When you type a URL into a web browser, this is what happens:
Transmission Control Protocol TCP is responsible for routing application protocols to the correct application on the destination computer. TCP is located under the application layer in the protocol stack is the TCP layer. When applications open a connection to another computer on the Internet, the messages they send (using a specific application layer protocol) get passed down the stack to the TCP layer. To accomplish this, port numbers are used. Ports can be thought of as separate channels on each computer. For example, you can surf the web while reading e-mail. This is because these two applications (the web browser and the mail client) used different port numbers. When a packet arrives at a computer and makes its way up the protocol stack, the TCP layer decides which application receives the packet based on a port number. Internet Protocol IP's job is to send and route packets to other computers. IP packets are independent entities and may arrive out of order or not at all. It is TCP's job to make sure packets arrive and are in the correct order. Complete packet
3. "E-Commerce Sellers Should be Preemptive to Mitigate Effects of Account Suspensions for IP Infringement Cybersecurity Law & Strategy Journal May 2022 "
Please note that the numbers below refer to chapters in 101 Things You Need To Know About Internet Law by Jonathan Bick (Random House 2000) copy on Canvas.
Start research logs and outlines II September 1 Internet Technology and Internet Law Models
1. "Domain Names Yield Novel Legal Difficulties" New Jersey Law Journal March 24, 2022 2. “Making Director and Shareholder Virtual Meetings Secure” Cybersecurity Law and Strategy December 2, 2020 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/DirectorandShareholdervirtualmeetingcybersecurity.htm 3. “Cybersecurity: A Combination of Legal, Business and Technical Measures” October 25, 2019 New Jersey Law Journal http://bicklaw.com/Publications/Cybersecurity.htm 4. "Internet Man in the Middle Attack" Internet Law and Strategy January 29, 2016;http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ManintheMiddleAttacks.htm 5. “Judicial Notice and the Internet: The Legal Reasoning and Technical Basis for Taking Judicial Notice of the Fact that Internet Pages Display from the Top-Left-Hand Corner Out” Washburn Law Journal Spring 2013; http://www.bicklaw.com/JudicalNotice_000.htm 9. “Viable E-signature Options” The Copyright & New Media Law Newsletter July 2004; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Viable_e-signature.htm Review Text Topics … Chapters 11 – 20 … Please note that the numbers which follow refer to chapters in 101 Things You Need To Know About Internet Law by Jonathan Bick (Random House 2000) copies in Library 11. Trademark names and e-linking are subject to legal scrutiny ; 12. Internet banking is legal; 13. Unencrypted Internet communication is not usually protected by attorney-client privilege; 14. Internet business methods can be patented; 15. License don't sell-Internet domain names; 16. Internet privacy rights are scarce; 17. E-commerce data collection is subject to legal limitations ; 18. The Constitution limits a court's ability to make an Internet site owner subject to an out-of-state suit; 19. Internet repossessions are legal; 20. Internet service providers (ISPs) are protected from legal liability for certain actions of their clients Hand in copy of research log review (optional) III September 8 Privacy
2. “Internet Legal Ethics and Client Privacy” New Jersey Law Journal ,http://www.bicklaw.com/Internetethics.htmJune 12, 2017 3. "E-Discovery Ethics: Let's Be Reasonable" New Jersey Law Journal May 4, 2016 http://bicklaw.com/E-DiscoveryEthics.htm 4. "ISP Access to E-mail Content: Not Invasion of Privacy" New Jersey Law Journal, November 9, 2011; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ISPAccess.htm 5. “Advances in Internet User Tracking Technology Yield New Privacy Violation Claims" New Jersey Law Journal February 21, 2011 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/tracking.htm 6. “Internet Diminishes Privacy Expectations and Torts” E-Commerce Law & Strategy April 2010; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InternetDiminishesPrivacy.htm 7. "Preserving Electronic Meeting Confidentiality" National Law Journal January 16, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ElectronicMeeting.htm 8. "E-Dissemination of Individual's Image" New Jersey Law Journal July 20 2009; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/E-DisofInvimage.htm
Review Text Topics … Chapters 21 – 30
IV September 15 Internet application to Jurisdiction, Regulation and related matters
2. "Product Liability Law Applies to Internet Products" New Jersey Law Journal December 8, 2017; http://www.bicklaw.com/InternetProductLiability.htm 3. “Application of Bankruptcy Law to Internet Assets” New Jersey Law Journal February 20, 2017 http://www.bicklaw.com/ApplicationofBankruptcyLawtoInternetAssets.htm 4. "Improper Internet Use Exacerbates Malpractice Exposure" New Jersey Law Journal January 20, 2015; http://bicklaw.com/Publications/Malpractice.htm 5. "How Internet Use Can Ameliorate Mass-tort Litigation Difficulties" New Jersey Law Journal December 16, 2013; http://bicklaw.com/Publications/E-masstortlitigation.htm 6. "Cyber Rentals" New Jersey Law Journal April 24, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/CyberRentals.htm 7. Internet Coming into Play - Internet and Real Estate New York Law Journal, August 14, 2000; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Internet_commin_into_play.htm 8. "Internet Job Application Regulations" New Jersey Law Journal March 6, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InternetJobApplicationRegulations.htm 9. E Self Help New Jersey Law Journal September 30, 2002 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/e-self_help.htm 10 . Zippo Mfg. Co. v. Zippo DOT Com, 952 F. Supp. 1119 (1997) The court created a sliding scale of purposeful availment based on the interactivity of the defendant's Internet activities. A complaint alleging trademark dilution, infringement and false designation. A motion to dismiss for lack of personal jurisdiction and improper venue, was made. Court found purposeful availment because Defendant had contracted with numerous individuals and Internet access providers in Pennsylvania and the intended object of the transactions had been the downloading of electronic messages that formed the basis of suit in Pennsylvania. 11. Top HR E-Laws New Jersey Law Journal June 9, 2003 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Top_HR_e-laws.htm 12. E-Cyber Squatting New Jersey Law Journal December 2, 2002 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/e-cyber_squatting.htm
Outlines returned with comments (not graded ) V September 22 Intellectual Property - Trademarks, Copyrights and Patents
2. Internet Content Rights Arise Upon Publication New Jersey Law Journal January 14, 2021 http://www.bicklaw.com/InternetContentRights.htm 3. "Abusive Social Networking Can Yield Intellectual Property Infringement" e-Commerce Law & Strategy October 2010 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Abuse.htm 4. “Using Ethic Rules in Malpractice Proceedings to Protect Confidential Intellectual Property” January 08, 2020 New Jersey Law Journal http://bicklaw.com/Publications/eithics.htm 5. "Five Ways to Make Your Internet Idea Patentable" New Jersey Business June 2019 http://www.bicklaw.com/Internetpatent.htm; 6. “Copyright Law Change Endangers Internet Sites” New Jersey Law Journal December 26, 2016http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/CopyrightLawChangeEndangersInternetSites.htm 7. "Copyright Law Protects Big Data" Internet Law and Strategy, May 5, 2015 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/BigData.htm 8. "Internet Copyright Troll" Internet Law & Strategy Volume 21, Number 2 • November 2014 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InternetCopyrightTrolls.htm 9. "The Maturing Nature of e-Intellectual Property Legal Services" New Jersey Law Journal November 12, 2012;http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/newservice.htm 10. "Lawful Use of Internet Keywords" New Jersey Law Journal April 10, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/LawfulUseofInternetKeywords.htm 11. "Internet-Based Franchise Encroachment Runs Rampant" New Jersey Law Journal December 20, 2010 http://www.bicklaw.com/e-Franchiseproblems.htm 12. Licensing Domain Name New York Law Journal, August 24, 1999 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/License_domain_Name.htm 16. METRO-GOLDWYN v. GROKSTER, LTD., 125 S. Ct. 2764; 162 L. Ed. 2d 781; June 27, 2005 -- Software distributors contended that they could not be liable for the users' infringements since the software was capable of substantial non-infringing uses. The U.S. Supreme Court found software was distributed with object of promoting infringement. Review Text Topics … Chapters 41 – 50 41. Most proposed Internet legislation is not likely to be implemented ;42. Digital certificates do not usually provide significant legal rights ;43. Internet loans are lawful ;44. Internet insurance addresses new risk ;45. Internet wagering is generally illegal ;46. Some Internet content is legally free to use ;47. Internet nondisclosure agreements have unique features ;48. Internet investment advisers require special legal precautions ;49. Taxation of European e-commerce differs among countries ;50. Using Internet materials may increase legal risk VI September 29 Speech / Censorship 1. "Cloud Content Is Copyright Protected; But Its Providers Are Not" New Jersey Law Journal July 27, 2015; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/CloudContentIsCopyrightProtected.htm 2. Combating Gripe Site Difficulties" New Jersey Law Journal February 25, 2015 http://www.bicklaw.com/Gripesite.htm 3. “Old vs. New: Bloggers Want Same Rights as Mass Media" New Jersey Law Journal August 22, 2013; http://bicklaw.com/oldblogers.htm 4. "Identifying Unnamed Online Speakers Just Got Easier" New Jersey Law Journal May 13, 2013; http://www.bicklaw.com/IDE-speakers.htm 5. "Anonymous Versus Fraudulent Internet Speech" New Jersey Law Journal September 12, 2012; http://www.bicklaw.com/speechandfraud.htm 6. "E-Speech Becoming Semi-free Speech" New Jersey Law Journal April 21, 2008; http://www.bicklaw.com/E-speechsemi-free.htm 7. "Surfing at the Library Could Get Less Restrictive" New Jersey Law Journal January 30, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/PublicLibraryInternet.htm 8. American Libraries Ass'n v. Pataki, 969 F. Supp. 160 (S.D.N.Y. June 20, 1997). 9. “Political Spam” New Jersey Law Journal February 7, 2005 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/PoliticalSpam.htm 10. In Dow Jones & Co. v. Gutnick, Australia High Court [2002] H.C.A. 56 The Australian High Court held that Australian courts have jurisdiction over a claim of defamation based on material that was placed on the Internet outside of Australian borders. http://www.securitymana gement.com library/Dow_Gutnick0403.pdf#search='Dow%20Jones%20&%20 Co.%20v.%20Gutnick' (last visited 8/1/05) 11. “E-Broadcast” New Jersey Law Journal July 22, 2003 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/e-broadcast.htm 12. Reno v. ACLU, 521 U.S. 844 (U.S., 1997) The Supreme Court has rejected attempts to extend the broadcast regime to the Internet. 13. "Protecting Bloggers from Liability" New Jersey Law Journal September 26, 2011; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ProtectingBloggers.htm 14. “Federal Trade Commission Regulates Blogging" New Jersey Law Journal November 30, 2009; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/bloggers-ftc.htm; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ProtectingBloggers.htm Review Text Topics … Chapters 51 – 60 … 51. E-business is particularly susceptible to nine legal perils; 52. International program license agreements are important for e-commerce outside of the U.S; 53. The responsibility for content control by Internet service providers varies in Europe; 54. Some countries legally protect personal data stored on the Internet; 55. Worldwide Internet e-data legal protection varies; 56. Internet signatures can be legally acceptable; 57. Internet patents are subject to legal testing; 58. Internet proxies are lawful; 59. Internet intellectual property transfers must apply state law.... ; 60. Internet message encryption laws diverge
VII October 6 Torts 1. "Need to Repair Your Online Reputation? There Are Laws for That" New Jersey Law Journal November 30, 2018 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ReputationRepair.htm; 2. "Using Communication Decency Act and Promissory Estoppel to Combat Internet Defamation" New Jersey Law Journal April 7, 2016; http://www.bicklaw.com/CDA.htm 3. "Improper Internet Use Exacerbates Malpractice Exposure" New Jersey Law Journal January 20, 2014; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Malpractice.htm 6. Protecting Internet Communications New Jersey Law Journal January 17, 2005 http://bicklaw.com/Publications/ProtectingInternetCommunications.htm Review Text Topics … Chapters 61 – 70 61. Internet chemical purchases are subject to recipients' jurisdictional rules 62. International e-privacy laws are primarily voluntary 63. International e-copyright laws are in flux 64. Clicking "I agree" has different meanings around the world ... 65. Global e-buyers beware 66. International e-broadcasting legal rules are country specific.. 67. Special legal liability is associated with e-promotions 68. Typical domain name cease-and-desist letter and an appropriate reply 69. Reply to domain name cease-and-desist letter 70. FCC has begun to regulate the Internet
VIII October 13 Criminal Law 1. Inside Cryptocurrency Pump-and- Dump Schemes" Cybersecurity Law & Strategy Journal February 2022; 2.“Internet Content Changes White-Collar Criminal Litigation Tactics” New Jersey Law Journal August 8, 2016http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InternetContentChangesWhite-CollarCriminalLitigationTactics_000.htm 3. "Courts Allow Broader Search Warrants for Internet Crimes, New Jersey Law Journal August 10, 2015; http://www.bicklaw.com/SearchWarrants.htm 4."Internet Copyright Infringement: An Emerging White-Collar Crime Internet" August 7, 2014 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InternetCopyrightInfringement.htm
IX October 20 Death and Taxes
2. Estate Planning in the Age of Cryptocurrency" New Jersey Law Journal April 23, 2018;http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/EstatePlanningintheAgeofCryptocurrency.htm 3. All Digital Assets are Not Legally Equivalent" New Jersey Law Journal October 2, 2017http://www.bicklaw.com/Internetassets.htm; 4. “Who Inherits Your E-mail?" New Jersey Law Journal June 5, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InheritE-mail.htm
X October 27 Elements of electronic commerce 1. How to Protect a Website's Legal Identity" The Intellectual Property Strategist February 2022; 2. "Internet Document Access May Justify Additional Settlement Clause" New Jersey Law Journal June 17, 2021 3. “Good Faith and Fair Dealing Bar to Abusive Online Reviews” January 29, 2021 New Jersey Law Journal http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/AbusiveInternetPosting.htm 4. "Contract and Tort Law (Not Property) Are Required for Blockchain Property Transactions" New Jersey Law Journal June 07, 2018 http://www.bicklaw.com/Contractandtortlawforblockchainproperty.htm 5. Are 'Smart Contracts' Smart Enough? -- Certain legal functions can be automated, particularly with the use of block chainshttp://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/AreSmartContractsSmartEnough.htm 6. "Treatment of Internet Licenses in Bankruptcy" New Jersey Law Journal February 10, 2015; http://www.bicklaw.com/TreatmentofInternet LicensesinBankruptcy.htm 7. "Existing Law Promotes Internet Advertising" New Jersey Law Journal April 1, 2013; http://www.bicklaw.com/ExistingLawPromotese-Adv.htm 8. "Enforceable Browse Wrap Contracts" New Jersey Law Journal September 14, 2009; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/browseWrap.htm 9. AMERICANS WITH DISABILITIES ACT AND THE INTERNET Copyright (c) 2000 Albany Law Journal of Science & Albany Law Journal of Science & Technology 2000; 10 Alb. L.J. Sci. & Tech. 205 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/ADA.htm 10. “Protection of Underage Internet Users Impacts E-Commerce” New Jersey Law Journal January 18, 2010; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Protection.htm 11. "Due Diligence for 'Dot-Com' Deals", Due Diligence New York Law Journal, May 18, 1999 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Due_diligence.htm 12. "Coping With COPPA New Jersey Law Journal December 29, 2003 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Coping_with_COPPA.htm 14. e-Dissemination The Internet Newsletter October 2001 volume 6, Number 7 American Lawyer Media -- Securities Law Avoiding the Violations Risked by Companies That Use the Web to Disseminate Information http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/e-dissemination.htm 15. Funding e-Firms The Daily Deal October 23, 2001 Copyright 2001 The Deal L.L.C. http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/funding%20e-firms.htm 16. Unauthorized Practice of Law Comm. v. Parsons Tech., Inc., 179 F.3d 956, 1999 U.S. App. LEXIS 14234 (5th Cir. Tex. 1999) -- Plaintiff moved to enjoin defendant corporation from selling and distributing software programs entitled "Quicken Family Lawyer." The district court granted the motion. The court vacated the injunction and judgment. The state legislature, subsequent to the filing of defendant's appeal, had enacted an amendment to Tex. Govt. Code Ann. § 81.101 (1998). The amendment, H.R. 1507, 76th Leg., Reg. Sess. (Tex. 1999), stated that the practice of law did not include the sale or distribution of computer software if the products stated clearly and conspicuously that the products were not a substitute for the advice of an attorney. 17. “Internet Merchant Service Agreements” September 2001 E-Commerce Supplement American Law Media http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Merchant_Service_Agreements.htm 18. "Internet Ticket Sales "New Jersey Law Journal November 14, 2005; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/E-tickets.htm 19. “Applying Technology to the Business of Health Care” New Jersey Law Journal April 30, 2012 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/E-BusinessofHealthcare.htm
XI November 3 International Law
2. "Integrating Trans-Atlantic Internet Medical Law" New Jersey Law Journal February 4, 2013; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/IntegratingTrans-AtlanticInternetMedicalLaw.htm 3. Protecting Domestic E-Commerce" May 31, 2010 New Jersey Law Journal http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/e-import.htm 4. "Overseas Courts Limit American Internet Speech" New Jersey Law Journal July 3, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/OverseasCourtsLimitAmericanE-Speech.htm 5. Course Materials 4 - Overseas Attorney View of E-Speech Restrictions -- response to "Overseas Courts Limit American Internet Speech" New Jersey Law Journal July 3, 2006; 6. Export Controls 7. Import Controls Text Topics … Chapter 101.Taxes apply to Internet transactions
XII November 10 Regulated activity - Gambling, Spam, and Drugs 1. "Internet Changes Medication Sales Regulations" Internet Law and Strategy Journal Volume 32, Number 5 February 2015 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/InternetChangesMedicationSalesRegulations.htm 2. "Selling Municipal Securities via the Internet" New Jersey Law Journal November 11, 2013; http://bicklaw.com/SellingMunicipalSecuritiesviatheInternet.htm 3. "Dual Use Spam" New Jersey Law Journal May 8, 2006; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/DualUseSpam.htm 4. Spammers Should Know Their Source New Jersey Law Journal April 11, 2005 http://www.bicklaw.com/SpamTargetSource.htm 5. Is your Client a Spammer? New Jersey Law Journal October 18, 2004 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/client_a_spammer.htm 6. Franchise Law Applies to Internet New Jersey Law Journal September 20, 2004 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/Franchise_Law.htm
XIII November 17 Student Presentations and special topics 1. Litigating Workplace Injuries in a Virtual Office" New Jersey Law Journal October 28, 2014 http://www.bicklaw.com/E-workplace.htm 2. "Applying Technology to the Business of Health Care" New Jersey Law Journal April 30, 2012; http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/E-BusinessofHealthcare.htm 3. Matrimonial Lawyers Have a New Tool New Jersey Law Journal January 3, 2005 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/e-MatrimonialLaw.htm 4. RIAA Suits The Internet Newsletter September 26, 2003 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/RIAA_Suits.htm 5. The Recording Industry Association of America Sues Its Members' Customers New Jersey Law Journal November 3, 2003 http://www.bicklaw.com/Publications/E-download_suits.htm 6. Internet Charity Registration Requirements New Jersey Law Journal May 9, 2005 http://www.bicklaw.com/InternetCharityRules.htm
Work product due (including: research logs, outlines, due in class, summary of meetings, draft of final work product, presentation notes / peer review comments and final work product)
|
|||